Introduction
The Routing Management is an aspect of the INIC Resources Management. Its responsibility is the connectivity between source and sink endpoints (see picture below).
A (virtual) route is a logical unidirectional connection between two endpoints. An endpoint acts as an INIC internal connection and consists of internal linked resources.
The routing management offers the following features:
- Create a route
- Destroy a route
- Monitor created routes and XRM resources
- Report each route state to the user application callback functions.
The UNICENS library provides therefore a set of functions to fulfill the above features. These will be depicted in the next sections.
Configuration
Since the routing management is based on XRM (refer to MNS V3.2.x), the user has to change the default values of the following macros to suit his specific system needs.
- UCS_NUM_REMOTE_DEVICES in
ucs_cfg.h - UCS_XRM_NUM_JOBS in
ucs_xrm_cfg.h - UCS_XRM_NUM_RESOURCES in
ucs_xrm_cfg.h
Initialization
The application shall provide following report callback functions in the UNICENS Init-Structure in order to receive any routing events. These are:
- rm.report_fptr: Optional callback function that reports status information for all routes. The passed result callback function does not only report the result of the build operation but also monitors the status of the created routes during their whole lifetime. That is, the callback function also reports the various states of a route (Refer to Ucs_Rm_RouteInfos_t for more infos). Furthermore the result of Ucs_Rm_SetRouteActive() function call is reported by this result callback function as well as the status of the ATD feature, if it is enabled for the route.
- Handling the states:
- Built: The route has been built. From this state a route can be deactivated respectively destroyed by the application or "auto-destroyed" if a system error occurs.
- Destroyed: The route has been destroyed successfully. The job has been instructed by the user application.
- Suspended: The route enters this state if critical configuration errors or temporary critical network errors occur or the maximum number of auto retries after uncritical errors has reached. The route will remain in this state until user intervention. The route can be reactivated by setting it to "inactive" first and than build the route again by setting it to "active".
- ATD Update available: An ATD update is available for the corresponding route. This is caused due to a route build event or the number of the nodes in the network changed.
- ATD Error: The ATD value could not be calculated for the corresponding route.
- rm.debug_resource_status_fptr: Optional callback function that acts as a debug interface for XRM resources. User application can monitor the specified XRM resources via this interface.
- rm.xrm.nw_port_status_fptr: Optional callback function that reports streaming-related information for the Network Port
- rm.xrm.check_unmute_fptr: Optional callback function that signals the EHC to check the mute pin state of devices before attempting an unmute.
- Example
- The code example illustrates how to initialize these callback functions: Ucs_InitData_t ucs_init_data;(void)Ucs_SetDefaultConfig(&ucs_init_data);/* Routing Management init section. */ucs_init_data.rm.report_fptr = &App_OnRoutingResult;ucs_init_data.rm.debug_resource_status_fptr = &App_OnDebuggingXrmResources;/* The report callback function for all routes */{/* Do whatever is necessary here */switch (route_infos){case UCS_RM_ROUTE_INFOS_BUILT:/* Route has been built */break;/* Route has been destroyed */break;/* Route can not be processed anymore due to UNICENS Termination */break;/* ATD update available *//* Do whatever is necessary here, e.g. Ucs_Rm_GetAtdValue() */break;/* ATD error occurred */break;default:/* Route has been suspended */break;}}/* Handle network Port Status event here */void App_Network_PortStatusCb(uint16_t nw_port_handle,Ucs_Network_PortAvail_t availability,Ucs_Network_PortAvailInfo_t avail_info,uint16_t free_streaming_bw,void* user_ptr){/* Do what needs to be.. */}/* Handle the Mute Pin check here */void App_CheckUnmuteStatusCb(uint16_t node_address, void *user_ptr){/* Check the state of the mute pin here before unmuting */}/* Debug interface for the XRM resources */void App_OnDebuggingXrmResources(Ucs_Xrm_ResourceType_t resource_type,Ucs_Xrm_ResObject_t *resource_ptr,Ucs_Xrm_ResourceInfos_t resource_infos,Ucs_Rm_EndPoint_t *endpoint_inst_ptr,void *user_ptr){switch (resource_infos){case UCS_XRM_INFOS_BUILT:/* Resource has been built */break;case UCS_XRM_INFOS_DESTROYED:/* Resource has been destroyed */break;case UCS_XRM_INFOS_ERR_BUILT:/* Resource cannot be built */break;default:/* Resource cannot be destroyed */break;}}
Operation
The basic handling of routing management is done by the supervisor. Have a look at the supervisors Normal Operation Mode Supervisor Normal Operation Mode. Nevertheless, the application can activate or deactivate specific routes using the Ucs_Rm_SetRouteActive() function.
It is important to note that, the build up of routes can take some time, in case the routing process may need to perform retries when uncritical errors occur (e.g.: transmission errors, processing errors, etc) or when certain conditions are not met yet (e.g. network not available, node not available, etc.). As an aside, the maximum number of retries is 0xFF and the minimum time between the retries is 50ms.
Also note that enabling the error and event trace output in ucs_cfg.h file (see below) will help user get detailed information on routes during processing.
Implementation Guide
The following example outlines the construction of a route between a local (Master) and a remote device inclusive the settings of the above preconditions. In this example the UCS_ADDR_LOCAL_NODE macro is used to address the local device and should only be used for the local device.
This example is inserted as a guide and may not contain all of the necessary details and information.
- Describing the route structure:
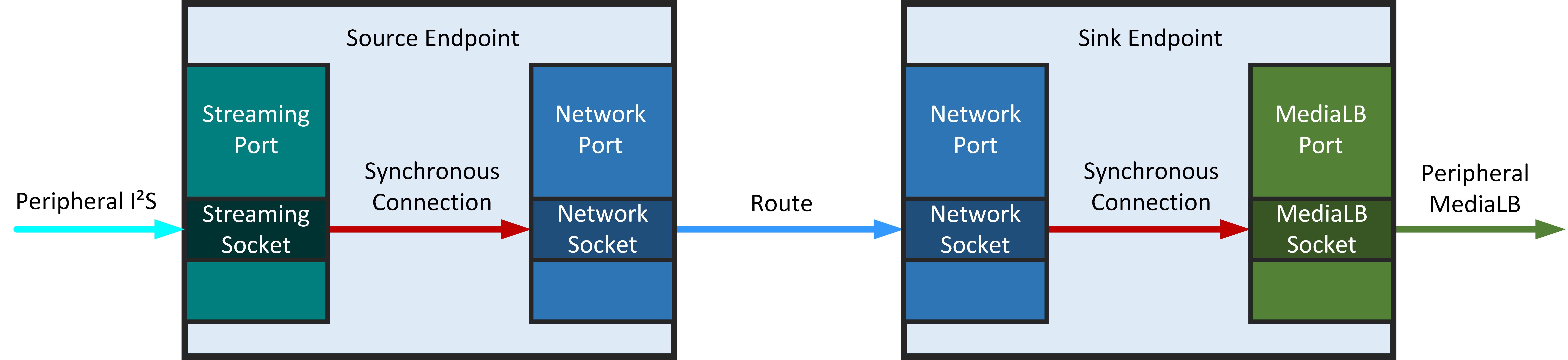
- In this section the route structure is defined for the route shown in the picture. Therefore XRM jobs have to be set for the needed resources in the sink and source endpoint.
- Implementation to build the defined route:
- The above defined route can be build by implementing and extending the following code example.
Additional Routing API
The Routing provides additional API functions to handle some runtime tasks. These functions are:
- Ucs_Rm_SetRouteActive() : This functions sets a specific route to
"active"or"inactive"at runtime. - Ucs_Rm_GetNodeAvailable() : This function retrieves the
"available"flag information of a given node. - Ucs_Rm_GetConnectionLabel(): This function retrieves the
ConnectionLabelof the given route.


