Challenges of security and privacy for people with cognitive disabilities
Web security and privacy technologies often block people with cognitive and/or physical disabilities who may not be able to:
- discern text they are required to enter and submit;
- recall text or instructions they have seen or heard;
- follow multi-step procedures.
The scope of the problem is vast because, for examples, people with disabilities:
- are prevented from purchasing goods and registering for services on the millions of websites that employ web security and privacy technologies;
- may circumvent web security and privacy technologies with insecure techniques/methods;
- may become so frustrated working through web security and privacy technologies that they relinquish their efforts, and thereby are thwarted from purchasing goods and registering for services;
- may be unable to become accustomed to a web security and privacy technology because there are multiple versions of it across websites.
-
may be afraid to trust a web site, thus causing them to cancel a transaction.
- Note: This is of particular concern for efforts to personalize web sites so they conform to users' accessibility preferences. (E.g., users may be asked whether they trust a web site in order to pass such preferences.) (See [[indie-ui-events]] and [[GPII-1]])
Memory
Many people with cognitive disabilities:
- may have to look at or listen to text several times to copy or type it into a form field;
- may not recall steps needed to complete a procedure if an authentication session expires;
- may reuse passwords;
- may use simple-to-remember passwords, which are easy to guess/determine;
- may keep passwords insecurely, such as written on pieces of paper;
- may not recall where they keep passwords (which may be found by people who should not have them).
Some people with cognitive disabilities may not:
- be able to recall required text, such as a password or a PIN, or remember how to retrieve it;
Executive function
Many people with cognitive disabilities may not:
- complete a multi-step procedure for submitting text, such as a password;
- complete a timed procedure due to slowness in completing all steps;
- complete a procedure even if provided multiple opportunities to do so;
- enter characters in the correct order;
- enter characters correctly on the first try (resulting in being locked out).
Some people with cognitive disabilities may not be able to:
- retrieve required text, such as a password or a PIN;
- determine the purpose of a web security and privacy technology sufficiently or at all.
Attention-related limitations
People with cognitive disabilities may not focus due to:
- frustration with time-limited procedures or presentations of digital security tokens;
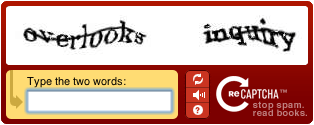
- irrelevant instructions, such as CAPTCHA's "stop spam" and "read books";
- presentation of multiple options, such as CAPTCHA's "Refresh", "Listen", and "Help".
Impaired language-related functions
Some people with cognitive disabilities:
- may have comprehension problems exacerbated by text or instructions presented in a non-native language.
Impaired literacy-related functions
Some people with cognitive disabilities:
- may not comprehend the meaning of instructions related to web security and privacy technologies;
- may, when presented with words by CAPTCHA, be at a disadvantage due to lack of word recognition or comprehension.
Perception-processing limitations
Many people with cognitive disabilities may not:
- read text at all because of the intentional distortion of it, a CAPTCHA technique;
- comprehend text that can't be enlarged without additional distortion;
- understand text spoken in a computerized and distorted voice, a CAPTCHA technique;
- recognize characters if they do not form words, or are shown in different fonts/styles.
Some people with cognitive disabilities may not:
- understand the purpose of buttons such as CAPTCHA's "reset", "listen", and "help";
- recognize functional elements, such as CAPTCHA's buttons, are clickable.
Reduced knowledge
Some people with cognitive disabilities may not:
- recognize images, such as symbols or icons, of web security and privacy technologies;
- comprehend the meaning of rich media designed to be instructive.