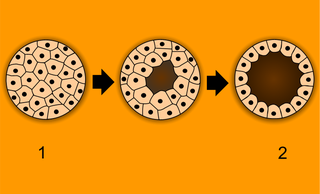
The zygote spends the next few days traveling down the Fallopian tube. As it travels, it divides by mitosis several times to form a ball of cells called a morula . The cell divisions, which are called cleavage , increase the number of cells but not their overall size. More cell divisions occur, and soon a fluid-filled cavity forms inside the ball of cells. At this stage, the ball of cells is called a blastocyst . The process of blastocyst formation is shown in Figure below.

The cells of the blastocyst form an inner and an outer cell layer. This is apparent in Figure below. The inner layer of cells is called the embryoblast. This layer of cells will soon develop into an embryo. The outer layer of cells is called the trophoblast. This layer will develop into other structures, including the placenta, which you will read more about below.
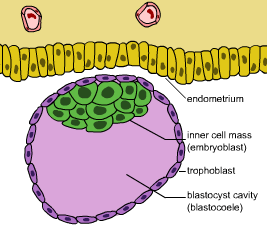
The blastocyst continues the trip down the Fallopian tube and reaches the uterus about four or five days after fertilization. When the outer cells of the blastocyst contact cells lining the uterus, the blastocyst embeds in the lining. The process of embedding is called implantation . It generally occurs about a week after fertilization. Once implantation occurs, the blastocyst is called an embryo.
Etc.
Etc.
Etc.
Etc.
Etc.
The measurements that scientists use are based on the International System of Units (SI), which is a form of the metric system. The term SI is shortened from the French term Le Système international d'unités . It is the world's most widely used system of units, both in science and business. It is useful to scientists because it is based on multiples of 10. The SI was developed in 1960 from an older metric system and is used in almost every country.
|
Name |
Symbol |
Quantity |
|
meter |
m |
length |
|
kilogram |
kg |
mass |
|
second |
s |
time |
|
ampere |
A |
electric current |
|
kelvin |
K |
thermal energy (temperature) |
|
mole |
mol |
amount of substance |
|
candela |
cd |
luminous intensity |
A prefix may be added to SI units to make a multiple of the original unit.
|
Name |
Symbol |
Factor of 10 |
Name |
|
tera- |
T |
1,000,000,000,000 (10 12 ) |
trillion (thousand billion) |
|
giga- |
G |
1,000,000,000 (10 9 ) |
billion (thousand million) |
|
mega- |
M |
1,000,000 (10 6 ) |
million |
|
kilo- |
k |
1000 (10 3 ) |
thousand |
|
hecto- |
h |
100 (10 2 ) |
hundred |
|
deca- |
da |
10 (10 1 ) |
ten |
|
deci- |
d |
1 (10 -1 ) |
tenth |
|
centi- |
c |
0.1 (10 -2 ) |
hundredth |
|
milli- |
m |
0.01 (10 -3 ) |
thousandth |
|
micro- |
µ |
0.00001 (10 -6 ) |
millionth |
|
nano- |
n |
0.00000001 (10 -9 ) |
billionth |
|
pico- |
p |
0.00000000001 (10 -12 ) |
trillionth |
Etc.
Etc.
Etc.
Etc.
Etc.