Write your own R functions, part 1
What and why?
My goal here is to reveal the process a long-time useR employs for writing functions. I also want to illustrate why the process is the way it is. Merely looking at the finished product, e.g. source code for R packages, can be extremely deceiving. Reality is generally much uglier … but more interesting!
Why are we covering this now, smack in the middle of data aggregation? Powerful machines like dplyr, purrr, and the built-in apply family of functions, are ready and waiting to apply your purpose-built functions to various bits of your data. If you can express your analytical wishes in a function, these tools will give you great power.
Load the Gapminder data
As usual, load the Gapminder data.
library(gapminder)
str(gapminder)
## Classes 'tbl_df', 'tbl' and 'data.frame': 1704 obs. of 6 variables:
## $ country : Factor w/ 142 levels "Afghanistan",..: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
## $ continent: Factor w/ 5 levels "Africa","Americas",..: 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 ...
## $ year : int 1952 1957 1962 1967 1972 1977 1982 1987 1992 1997 ...
## $ lifeExp : num 28.8 30.3 32 34 36.1 ...
## $ pop : int 8425333 9240934 10267083 11537966 13079460 14880372 12881816 13867957 16317921 22227415 ...
## $ gdpPercap: num 779 821 853 836 740 ...Max - min
Say you’ve got a numeric vector, and you want to compute the difference between its max and min. lifeExp or pop or gdpPercap are great examples of a typical input. You can imagine wanting to get this statistic after we slice up the Gapminder data by year, country, continent, or combinations thereof.
Get something that works
First, develop some working code for interactive use, using a representative input. I’ll use Gapminder’s life expectancy variable.
R functions that will be useful: min(), max(), range(). Read their documentation.
## get to know the functions mentioned above
min(gapminder$lifeExp)
## [1] 23.599
max(gapminder$lifeExp)
## [1] 82.603
range(gapminder$lifeExp)
## [1] 23.599 82.603
## some natural solutions
max(gapminder$lifeExp) - min(gapminder$lifeExp)
## [1] 59.004
with(gapminder, max(lifeExp) - min(lifeExp))
## [1] 59.004
range(gapminder$lifeExp)[2] - range(gapminder$lifeExp)[1]
## [1] 59.004
with(gapminder, range(lifeExp)[2] - range(lifeExp)[1])
## [1] 59.004
diff(range(gapminder$lifeExp))
## [1] 59.004Internalize this “answer” because our informal testing relies on you noticing departures from this.
Skateboard >> perfectly formed rear-view mirror
This image widely attributed to the Spotify development team conveys an important point.
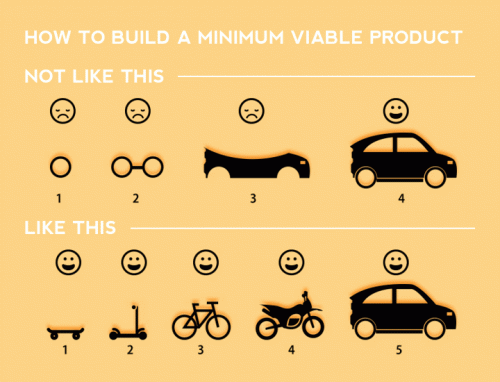
Build that skateboard before you build the car or some fancy car part. A limited-but-functioning thing is very useful. It also keeps the spirits high.
This is related to the valuable Telescope Rule:
It is faster to make a four-inch mirror then a six-inch mirror than to make a six-inch mirror.
Turn the working interactive code into a function
Add NO new functionality! Just write your very first R function.
max_minus_min <- function(x) max(x) - min(x)
max_minus_min(gapminder$lifeExp)
## [1] 59.004Check that you’re getting the same answer as you did with your interactive code. Test it eyeball-o-metrically at this point.
Test your function
Test on new inputs
Pick some new artificial inputs where you know (at least approximately) what your function should return.
max_minus_min(1:10)
## [1] 9
max_minus_min(runif(1000))
## [1] 0.997364I know that 10 minus 1 is 9. I know that random uniform [0, 1] variates will be between 0 and 1. Therefore max - min should be less than 1. If I take LOTS of them, max - min should be pretty close to 1.
It is intentional that I tested on integer input as well as floating point. Likewise, I like to use valid-but-random data for this sort of check.
Test on real data but different real data
Back to the real world now. Two other quantitative variables are lying around: gdpPercap and pop. Let’s have a go.
max_minus_min(gapminder$gdpPercap)
## [1] 113282
max_minus_min(gapminder$pop)
## [1] 1318623085Either check these results “by hand” or apply the “does that even make sense?” test.
Test on weird stuff
Now we try to break our function. Don’t get truly diabolical (yet). Just make the kind of mistakes you can imagine making at 2am when, 3 years from now, you rediscover this useful function you wrote. Give your function inputs it’s not expecting.
max_minus_min(gapminder) ## hey sometimes things "just work" on data.frames!
## Error in FUN(X[[i]], ...): only defined on a data frame with all numeric variables
max_minus_min(gapminder$country) ## factors are kind of like integer vectors, no?
## Error in Summary.factor(structure(c(1L, 1L, 1L, 1L, 1L, 1L, 1L, 1L, 1L, : 'max' not meaningful for factors
max_minus_min("eggplants are purple") ## i have no excuse for this one
## Error in max(x) - min(x): non-numeric argument to binary operatorHow happy are you with those error messages? You must imagine that some entire script has failed and that you were hoping to just source() it without re-reading it. If a colleague or future you encountered these errors, do you run screaming from the room? How hard is it to pinpoint the usage problem?
I will scare you now
Here are some great examples STAT545 students devised during class where the function should break but it does not.
max_minus_min(gapminder[c('lifeExp', 'gdpPercap', 'pop')])
## [1] 1318683072
max_minus_min(c(TRUE, TRUE, FALSE, TRUE, TRUE))
## [1] 1In both cases, R’s eagerness to make sense of our requests is unfortunately successful. In the first case, a data.frame containing just the quantitative variables is eventually coerced into numeric vector. We can compute max minus min, even though it makes absolutely no sense at all. In the second case, a logical vector is converted to zeroes and ones, which might merit an error or at least a warning.
Check the validity of arguments
For functions that will be used again – which is not all of them! – it is good to check the validity of arguments. This implements a rule from the Unix philosophy:
Rule of Repair: When you must fail, fail noisily and as soon as possible.
stopifnot
stopifnot() is the entry level solution. I use it here to make sure the input x is a numeric vector.
mmm <- function(x) {
stopifnot(is.numeric(x))
max(x) - min(x)
}
mmm(gapminder)
## Error in mmm(gapminder): is.numeric(x) is not TRUE
mmm(gapminder$country)
## Error in mmm(gapminder$country): is.numeric(x) is not TRUE
mmm("eggplants are purple")
## Error in mmm("eggplants are purple"): is.numeric(x) is not TRUE
mmm(gapminder[c('lifeExp', 'gdpPercap', 'pop')])
## Error in mmm(gapminder[c("lifeExp", "gdpPercap", "pop")]): is.numeric(x) is not TRUE
mmm(c(TRUE, TRUE, FALSE, TRUE, TRUE))
## Error in mmm(c(TRUE, TRUE, FALSE, TRUE, TRUE)): is.numeric(x) is not TRUEAnd we see that it catches all of the self-inflicted damage we would like to avoid.
if then stop
stopifnot() doesn’t provide a very good error message. The next approach is very widely used. Put your validity check inside an if() statement and call stop() yourself, with a custom error message, in the body.
mmm2 <- function(x) {
if(!is.numeric(x)) {
stop('I am so sorry, but this function only works for numeric input!\n',
'You have provided an object of class: ', class(x)[1])
}
max(x) - min(x)
}
mmm2(gapminder)
## Error in mmm2(gapminder): I am so sorry, but this function only works for numeric input!
## You have provided an object of class: tbl_dfIn addition to a gratuitous apology, the error raised also contains two more pieces of helpful info:
- Which function threw the error.
- Hints on how to fix things: expected class of input vs actual class.
If it is easy to do so, I highly recommend this template: “you gave me THIS, but I need THAT”.
Wrap-up and what’s next?
Here’s the function we’ve written so far:
mmm2
## function(x) {
## if(!is.numeric(x)) {
## stop('I am so sorry, but this function only works for numeric input!\n',
## 'You have provided an object of class: ', class(x)[1])
## }
## max(x) - min(x)
## }What we’ve accomplished:
- we’ve written our first function
- we are checking the validity of its input, argument
x - we’ve done a good amount of informal testing
Where to next? In part 2, we generalize this function to take differences in other quantiles and learn how to set default values for arguments.
Resources
Packages for runtime assertions (the last 3 seem to be under more active development than assertthat):
assertthaton CRAN and GitHub the Hadleyverse optionensureron CRAN and GitHub general purpose, pipe-friendlyassertron CRAN and GitHub explicitly data pipeline orientedassertiveon CRAN and Bitbucket rich set of built-in functions
Hadley Wickham’s book Advanced R
- Section on defensive programming
