HTTP- HyperText Transfer Protocol
Learning Object
Linnaeus University


Licence for this work
This work is produced by John Häggerud at Linnaeus University.
All content in this work excluding photographs, icons, picture of course litterature and Linnaeus University logotype and symbol, is licensied under a

Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
You are free to
- copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- spread the whole or parts of the content
- show the whole or parts of the content publicly and digital
- convert the content to another format
- change the content
If you change the content do not use the photographs, icons, picture of the course literature or Linnaeus University logotype and symbol in your new work!
At all times you must give credit to: ”Linnaeus university” with the link https://webbprogrammerare.se and to the Creative Common-license above.
Tim Berners-Lee

Paul Clarke [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
CERN httpd


Web server session
In order to associate a request to any other request, you need a way to store user data between HTTP/HTTPS requests.
- The user send the state information with every request (state on client)
- http://www.example.com?id=1023&username=thajo
- Cookie with all the data
- Let the user send a "secret" id and let the server store the session data
- http://www.example.com?id=sdhjH223Hsjhdj2jasdlj
- Session cookie - encrypted or a hash
- A by the server(s) signed token (JSON Web Token)
Requests and TCP connections
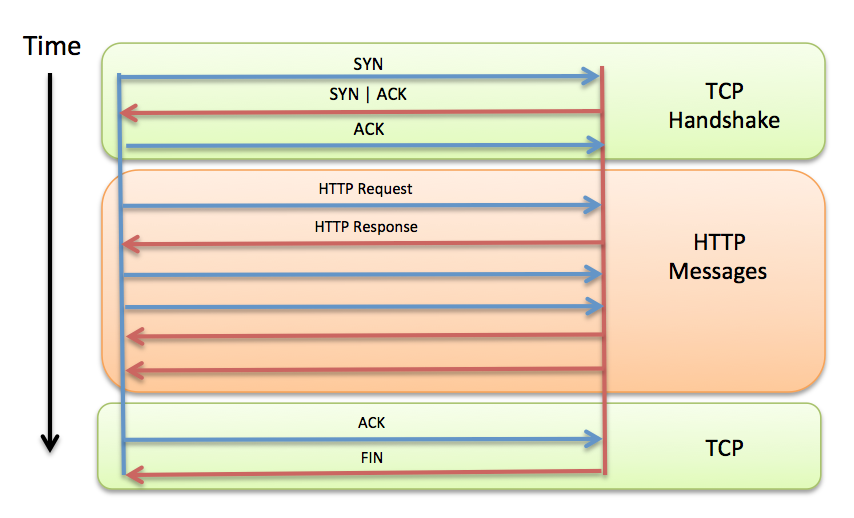
- Keep-Alive, Pipeline (HTTP 1.1)